What Is The Measurement Of A Candle?
Introduction
Candle measurements are important for ensuring consistent quality, performance, and sizing across candle production. Standardized candle sizes allow consumers to have clear expectations when purchasing candles, and they enable candle makers to produce and market their products effectively. There are several key measurements that are tracked in candle making.
Measuring items such as candle wicks, wax, density, diameter and fragrances provides important data to guarantee high quality and consistent characteristics. There are candle testing standards and specifications that many manufacturers adhere to. Understanding key candle measurements helps buyers choose the right candles for their needs and allows producers to efficiently formulate and manufacture candle products. This overview will look at the common measurements used in the candle industry.
Basic Units of Candle Measurement
There are several standard units used to measure different aspects of a candle:
Inches: Length measurements like candle height and diameter are usually measured in inches. Most candles fall within a height range of 2-6 inches. Taller novelty candles may be over 12 inches high. Candle diameter is measured across the top and can range from less than 1 inch for birthday candles, to over 3 inches for large pillars.
Pounds: Candle wax weight is measured in pounds or fractions of a pound. A standard container candle holds about .33 to 1 pound of wax. Large pillars may hold over 2 pounds of wax.
Wick height: The height of the wick, measured in inches above the top of the candle wax, helps determine how large and bright the candle’s flame will be. Most wicks protrude about .25-.5 inches above the wax.
So in summary, common units used in candle measurement are inches, pounds, diameter and height.
Standard Candle Sizes
When shopping for candles, you’ll notice they come in standard sizes. Some of the most common candle sizes include:
Birthday Candles
Birthday candles are very thin, generally measuring 0.5-0.75 inches in diameter and 4-5 inches tall. They are designed to fit neatly on top of a birthday cake and burn for a short time.
Votive Candles
Votive candles are short and squat, with a diameter around 1.5-2 inches and height from 2-3 inches. Votives melt to form a deep wax pool and are popularly used in candle holders.
Pillar Candles
Pillar candles are thicker cylindrical candles designed to stand upright. They range from 2-3 inches in diameter and can be anywhere from 4 inches to several feet tall. Pillars are measured by diameter and height.
Tapers
Tapers are long, thin candles with diameters generally between 0.5-1 inch. They are taller than votives, usually 6-12 inches high. Tapers are designed to fit into candlesticks and taper holders.
Measuring Candle Wicks
The wick is one of the most important parts of a candle. The thickness and length of the wick determines how the candle will burn. Wick diameter and length need to be properly measured and matched to the candle size and wax type.
For wick diameter, most candle wicks range between 1/16 inches to 1/4 inches thick. Smaller candles like votives and tapers often use smaller wick diameters around 1/16 or 3/32 inches. Larger pillar and container candles will need thicker wicks closer to 1/4 inches in diameter to burn properly.
Wick length is also a key factor. The wick needs to be trimmed to 1/4 to 1/2 inch above the top of the candle. Long wicks will create excess soot and smoke. Short wicks can tunnel or drown in melted wax. Properly measuring and trimming the wick before burning is essential.
Testing is needed to find the optimal wick size for a particular wax and fragrance formula. The diameter and length will impact how quickly wax is drawn up and how bright and high the flame burns. Following manufacturing guidelines and testing different wicks are the best ways to achieve the right sizing.
Measuring Candle Wax
The most common types of wax used in candle making are paraffin, soy wax, beeswax, and palm wax. Each wax has different properties that affect how they should be measured.
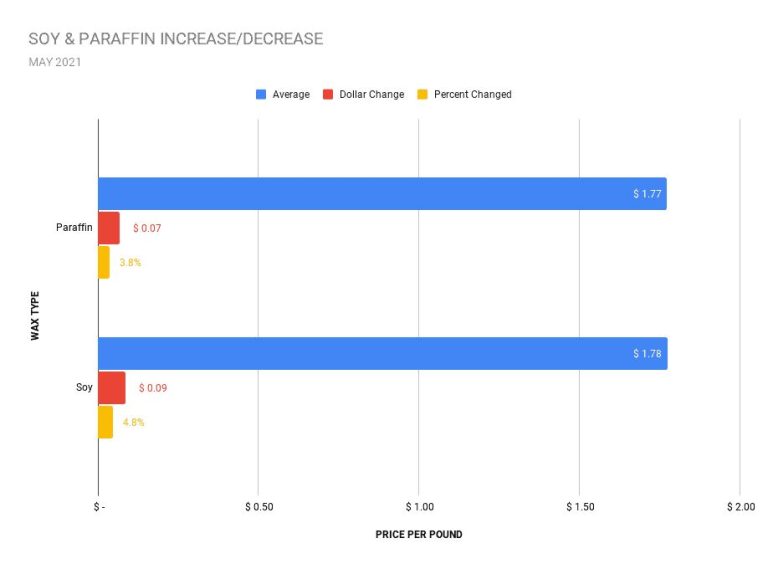
Paraffin wax is a petroleum byproduct that comes in slab form. It is typically measured in pounds or kilograms. The density of paraffin can range from 0.9 – 0.98 g/cm3 depending on the type of paraffin used. Measuring paraffin by weight gives candle makers precise control over candle specifications.
Soy wax is made from hydrogenated soybean oil. It comes in flake and pellet form. Soy wax is also commonly measured by weight in pounds or kilograms. Its density ranges from 0.9 – 1 g/cm3. The density determines the soy wax’s melting point which impacts how the candle burns.
Beeswax is 100% natural wax produced by honey bees. Beeswax is sold in blocks by weight or volume. Its density is around 0.96 g/cm3. Since beeswax has a high melting point compared to other waxes, measuring by weight is recommended for accuracy.
Palm wax comes from the fruit of palm trees. It is available in flake form and measured by weight in pounds or kilograms. Palm wax density can vary between 0.79 – 0.98 g/cm3. The density affects the palm wax’s crystallization properties in candle making.
Precisely measuring wax by weight helps candle makers fine-tune the wax blend to achieve the desired burn properties. Knowing the density also allows calculating the ratio of wax to fragrance oil.
Candle Density and Burn Time
The density of a candle’s wax plays an important role in determining how long a candle will burn. Dense wax with tightly packed molecules will burn slower because it contains more wax in the same amount of volume. Less dense wax has fewer wax molecules in the same space, allowing oxygen to penetrate through the wax more quickly as it melts and vaporizes.
Testing burn time helps candle makers understand how different waxes, wicks, and vessel shapes affect total burn hours. To test burn time, candles are lit in a controlled setting and allowed to burn continuously until they extinguish on their own. The total time elapsed is the burn time. Some standard test methods specify minimum wearable height and diameter sizes to ensure consistent comparisons.
Factors like wax density, wax additives, wick type/size, melting point, vessel shape, and room temperature all impact burn time. Denser wax, larger wicks, higher melting points, smaller diameters, and lower room temperatures can all increase burn times. Test burn times help candle makers adjust their designs and achieve target burn times for different uses.
Candle Diameter and Height
The diameter and height of a candle play an important role in its structure and burn characteristics. There are some common ratios used for different types of candles:
- Pillar candles often have a diameter to height ratio of 1:3 to 1:4. This tall and narrow shape helps pillar candles burn slowly and prevents them from tunneling (creating a cavity around the wick as the wax burns).
- Votives and containers have a diameter to height ratio closer to 1:1 or 1:1.5. Their short, wide shape allows heat to disperse across the top of the wax pool as they burn.
- Tapers have a very tall, narrow shape with a diameter to height ratio of around 1:10 to 1:15. This allows tapers to burn slowly from top to bottom without issue.
In general, a candle needs a height of at least 2 inches per inch of diameter for stability. Short, wide candles can become top heavy as they burn and tall, narrow candles need adequate diameter to stand up on their own without tipping over. Testing different diameter-to-height ratios during candle development can ensure the proper balance is achieved for the candle’s intended use.
Measuring Candle Fragrances
Fragrance is an essential element of a candle that impacts the user experience. There are two main ways to measure fragrance in candles:
Fragrance Load
Fragrance load refers to the percentage of fragrance oil in a candle’s wax. This determines how strong the scent will be. Typical loads are 6-10% for pillar candles, and 10-12% for container candles. Higher loads above 15% can make candles unsafe and create excessive soot.
Scent Throw
Scent throw measures how far the fragrance disperses into the surrounding area when the candle is lit. Testing is done by burning a candle for a set time and distance, then evaluating scent dispersion and intensity. Candle wicks, wax type, room size and airflow all impact throw. A strong throw is desirable, but excessively strong scents can be overpowering in small spaces.
By optimizing fragrance load and scent throw, candle makers can create an ideal sensory experience for users.
Candle Testing Standards
There are several organizations that have developed standards for testing the quality and safety of candles. Some key candle testing standards to know include:
ASTM Standards
ASTM International sets numerous standards relating to candles. Some examples include:
- ASTM F2326 – Standard Test Method for Collection and Analysis of Visible Emissions from Candles as They Burn
- ASTM F2417 – Standard Specification for Fire Safety for Candles
- ASTM F4003 – Standard Specification for Fire Performance and Interaction of Components in End Items Employing Solid Burning Candles
These ASTM standards help ensure candles burn cleanly and safely.
IFRA Standards
The International Fragrance Association (IFRA) provides standards and recommendations for safely using fragrances in products like candles. IFRA candle standards help limit ingredient amounts to avoid potential sensitization or irritation.
Other Standards
Some other examples of candle testing standards include:
- ISO 15494 – Candles – Specification for sooting behaviour
- EN 15493 – Candles – Specification for burning behaviour
- UL 87 – Standard for Power-Operated Dispensing Devices for Petroleum Products
Adhering to appropriate standards helps ensure candle safety and performance.
Conclusion
In summary, there are several key measurements that are important when manufacturing high quality candles. The diameter and height help determine the size and burn time. Measuring the wick is crucial for proper candle performance – the wick must be sized appropriately to the candle diameter and wax type. The type and amount of wax impacts the candle’s density and burn characteristics. Finally, properly measuring and mixing candle fragrances is an art that affects the scent throw and burn experience.
Understanding these measurements allows candle makers to optimize their designs for aesthetics, performance, and safety. With the right balances of wax, wick, fragrance, and dimensions, manufacturers can craft premium candles that will delight and satisfy customers. Careful attention to candle measurements leads to a superior product that burns evenly, looks beautiful, and fills a room with fragrance.