What Was Paraffin Wax Used For?
Paraffin wax has been used by humans for centuries, dating back to ancient times. However, it became more widely produced and used during the 19th century as the petroleum industry evolved. Paraffin wax is derived from petroleum through the distillation process. It is a white or colorless soft solid that is composed of saturated hydrocarbons. Some of the key properties of paraffin wax include its melting point, high viscosity when melted, and waterproof nature. Historically, paraffin wax was utilized for applications like candles, cosmetics, food processing, medicine, art, lubrication, and waterproofing. It became a versatile material across many industries because of its unique chemical properties. Today, paraffin wax continues to have widespread uses, both in traditional applications as well as some more modern uses. This brief history provides an overview of how paraffin wax became an important material over time.
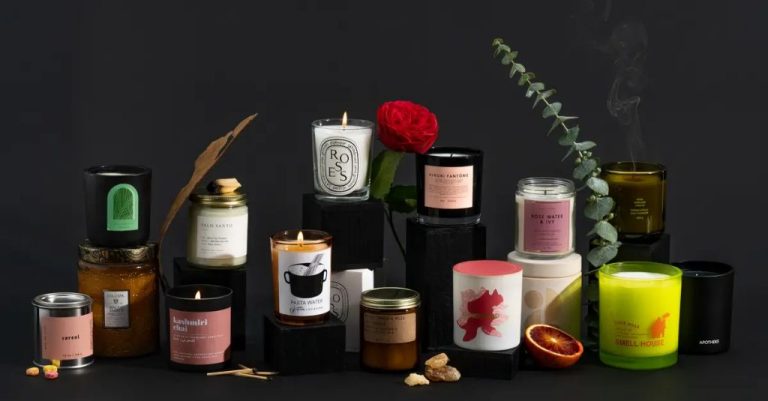
Candles
One of the most common uses of paraffin wax is in candle making. Paraffin wax has been used to make candles since the mid-1800s. It is desirable for candle making because it is colorless, odorless, and burns cleanly. Paraffin wax candles were a huge improvement over tallow candles, which produced a lot of smoke and unpleasant odors when burned.
According to the Yankee Candle Company, paraffin wax is a byproduct of petroleum refining. It has a melting point between 115-150°F, making it an ideal wax for container candles. Paraffin wax is highly refined and purified, producing an odorless and colorless wax that allows candle colors and scents to shine through. Compared to other waxes like soy and beeswax, paraffin wax is inexpensive, consistent in quality, and easy to work with. This makes it economical for large scale candle manufacturing.
To make paraffin candles at home, the wax is melted and mixed with candle dyes and fragrances as desired. Wicks are inserted into molds or containers before the melted wax is carefully poured in. Once cooled and set, the finished candles are ready to burn. Paraffin wax can also be used to make candle wax melts, tart candles, and votive candles. Its versatility and affordability make it a staple of both large commercial candle companies and home crafters.
While paraffin wax candles burn cleanly, some criticize them as being a petroleum product and not as natural as soy or beeswax candles. However, with proper wicking, paraffin candles release very little soot. The development of paraffin wax in the 19th century revolutionized candle making and enabled candles to be affordable enough for everyday use.
Cosmetics
Paraffin wax has been widely used in cosmetic and skin care preparations. It creates a smooth texture and provides a protective barrier on the skin. Some common cosmetic products containing paraffin wax include:
- Lip balms and lipsticks – It helps provide a smooth and glossy finish.
- Lotions and creams – It acts as an emollient to soften and moisturize the skin.
- Makeup foundations – It gives a velvet-like feel.
- Mascara – It thickens and lengthens eyelashes.

According to C.J. Robinson Co., Inc., paraffin wax conforms to FDA requirements for use in color cosmetics. It has a melting point of 55-57°C, making it suitable for cosmetic applications (https://gather.tracegains.com/market/paraffin-wax-c-j-robinson-co-inc). The semi-refined and fully refined grades are commonly used in cosmetics manufacturing (https://www.made-in-china.com/products-search/hot-china-products/Paraffin_Wax_Cosmetic.html). Overall, paraffin wax improves the texture, consistency and application of many cosmetic products.
Food
Paraffin wax has been widely used in food applications, especially for sealing and coating foods like cheese, baked goods, and candies. It helps prevent moisture loss, provides a protective barrier, and gives some foods a nice sheen or gloss. Food-grade paraffin wax meets purity standards for use in food, confirming it is odorless, tasteless, and non-toxic. Common food uses include:
– Coating chocolates, fruits, and cheeses to help preserve freshness and provide a shiny finish (https://paraffinwaxco.com/food-grade-paraffin-wax/).
– Sealing jars of jams, jellies, and preserves to prevent spoilage.
– Covering cut fruits like apples and pears to slow down browning.
– Making candies, giving them a waxy, chewy texture.
– Coating baking pans and molds to help release baked goods cleanly.
– Sealing wine corks and barrels.
Food-grade paraffin wax provides an edible, safe coating that helps extend the shelf life of many foods. It has been an important tool for commercial food production and home cooking for over a century.
Medicine
Paraffin wax has been used in various medical applications. It is often used to help with dry skin conditions as it can moisturize and soften the skin. According to TabletWise, paraffin wax can be applied topically to treat conditions like eczema, psoriasis, and xerosis (dry skin) as it creates an occlusive barrier that prevents moisture loss. This helps hydrate the skin and reduce scaling and inflammation. Paraffin wax treatments are also sometimes used by physical therapists to provide heat therapy for joint pain and stiffness. The warm wax helps relax muscles and increase blood flow. Paraffin wax is considered very safe for topical use.
Additionally, paraffin wax was historically used in pill coatings and as a binding agent for medicinal pills according to an overview from TabletWise. The inert wax coating helped mask tastes and facilitate swallowing. However, most modern pharmaceutical pills use alternative coatings and binding agents.
Sources:
https://www.tabletwise.net/medicine/paraffin-wax
Art
Paraffin wax has been an important material in art supplies and modeling. It is used to make modeling clay, crayons, and wax pastels because of its soft texture and ability to blend colors. Paraffin wax is also used in encaustic painting, where pigments are added to melted wax to create artwork. Encaustic painting dates back to 100 AD from the Fayum mummy portraits of Egypt.
Artists appreciate paraffin wax for modeling because it is pliable and easy to shape when warmed. Its low melting point makes it simple to remelt and reuse wax models. Paraffin’s light color also allows pigments to show through better. It can be carved and molded into detailed sculptures. Wax models are common preparations before casting metal or stone sculptures. Paraffin wax was likely used by Renaissance sculptors for modeling.
Today, paraffin wax remains popular for modeling wax, encaustic paints, and art supplies like crayons and colored pencils. It provides artists with a versatile, affordable, and workable material to create detailed artwork and sculpture. Sources: https://fineartamerica.com/art/paraffin+wax, https://fineartamerica.com/shop/prints/paraffin+wax
Lubrication
Paraffin wax has been used as a lubricant for many years. It provides lubrication through its slick, waxy texture that reduces friction between moving parts. Some of the key uses of paraffin wax as a lubricant include:
Machine lubrication – Paraffin wax can be applied to gears, bearings, slides, and other mechanical parts to keep the machinery running smoothly. It is a clean, non-staining lubricant. According to ShunBang Chemical Co., paraffin wax lubricant is commonly used in industry for lubricating machine parts.
Woodworking – Woodworkers often use paraffin wax to lubricate tools and other equipment. Rubbing paraffin wax on table saws, drill presses, router bits, and other tools helps prevent rust and reduces friction during use.
Locks and hinges – Applying paraffin wax to locks, door hinges, drawers, and other hardware helps keep them operating smoothly. The wax seeps into crevices to lubricate the moving parts inside. Some mechanics recommend using paraffin wax as a lubricant for tool drawers and hardware, according to discussions on GarageJournal.com.
Waterproofing
Paraffin wax has been widely used as a waterproofing agent for various materials. When applied to wood, leather, paper, and fabrics, paraffin wax creates a water-resistant barrier that prevents water absorption and damage. According to a study published on ResearchGate, paraffin wax emulsions effectively improved the water-repellent properties of wood when applied as a coating (https://www.researchgate.net/publication/231608529_Study_on_the_Effect_of_Raw_Material_Composition_on_Water-Repellent_Capacity_of_Paraffin_Wax_Emulsions_on_Wood). The paraffin wax fills in pores and creates a hydrophobic surface. This waterproofing ability made paraffin wax useful for preserving important documents and materials.
Preservation
Paraffin wax was historically used to help preserve biological specimens in a process called tissue fixation. In tissue fixation, paraffin is melted and tissues are immersed in the liquid wax. As the wax cools and solidifies it creates a paraffin block that can preserve the shape and structure of the tissue sample (Valchanov, 1998). This allows the tissue to be sectioned thinly using a microtome and mounted on microscope slides for pathological analysis. The paraffin provides a supporting matrix to maintain the integrity of the tissue. Paraffin’s hydrophobic properties also prevent the tissue from becoming distorted by water. This technique enabled the microscopic study of tissue structure and the development of fields like histology and histochemistry.
Conclusion
Paraffin wax played an important role throughout history, with a wide variety of uses across many industries. Its versatility made it a crucial material for candles, cosmetics, food preservation, medicine, art supplies, lubrication, waterproofing, and preservation.
Some of the main uses and importance of paraffin wax include:
- Candle making – it provided a cheap and effective fuel source for candles.
- Cosmetics – it was used in creams, ointments, and beauty products.
- Food preservation – it helped seal and extend the shelf life of fruits, cheese, and meat.
- Medicine – it was utilized for making ointments and salves.
- Art supplies – it was a key ingredient in modeling clay, crayons, and wax coloring pencils.
- Lubrication – its lubricating properties were harnessed for machines and industrial applications.
- Waterproofing – it provided effective waterproof coatings for many materials.
- Preservation – it helped preserve documents, artifacts, and delicate specimens.
Overall, paraffin wax proved to be an essential material throughout modern history due to its unique chemical properties, low cost, and versatility across many critical industries.