Is It Healthier To Burn Or Melt Candles?
There is an ongoing debate about whether it is healthier to burn or melt candles. Some argue that burning candles releases harmful substances like soot and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) into the indoor air. Meanwhile, others claim that melting candles avoids this indoor pollution. This article provides an overview of the debate and a comprehensive analysis of the health impacts of burning versus melting candles.
How Candles Burn
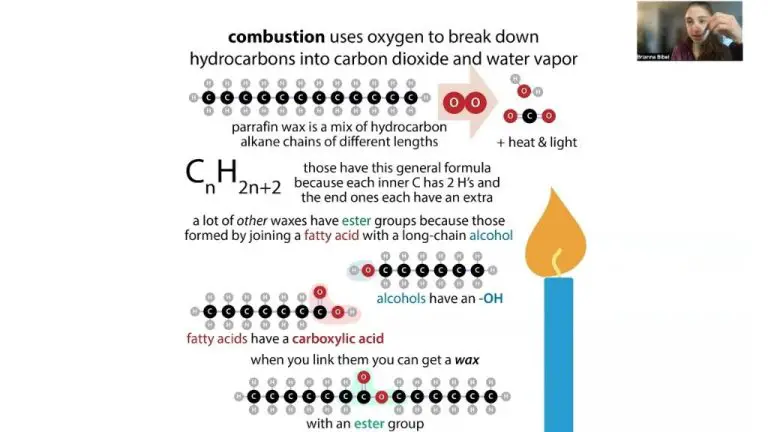
Candles burn through a chemical reaction called combustion. During combustion, the wick of the candle absorbs liquid wax and draws it up to the flame. The heat of the flame vaporizes the liquid wax into a hot gas. This gas mixes with oxygen in the air and undergoes an exothermic reaction, producing heat, light, water vapor, carbon dioxide, and soot (Source).
The visible flame that you see is actually hot gases undergoing combustion. The combustion produces several byproducts:
- Light – emitted from hot soot particles
- Heat – released from the exothermic reaction
- Water vapor – formed when the hydrocarbon molecules in wax react with oxygen
- Carbon dioxide – produced when carbon in wax bonds with oxygen
- Soot – unburned carbon particles that rise with hot gases
These byproducts are all released into the air around a burning candle. Some, like light, heat, and carbon dioxide are common results of combustion. Others, like soot and water vapor, are unique to candle wax. But all emerge due to the chemical reaction that sustains a candle’s flame.
Burning Releases Soot
When a candle burns, it releases soot which is made up of fine black particles that can irritate the lungs if inhaled ([1]). Soot is produced when the wax and wick don’t burn completely and only partial combustion occurs. The incomplete burning releases tiny unburnt carbon particles that make up the soot ([2]).
Studies show that breathing in candle soot can cause inflammation in the lungs and airways ([1]). The small soot particles are able to penetrate deep into the lungs, causing respiratory irritation. Over time, repeated exposure can lead to lung damage and breathing issues ([2]).
Melting Doesn’t Combust

Unlike burning, melting a candle does not create a combustion reaction. When you burn a candle, the wick ignites and the wax vaporizes in the heat, creating a small flame. This combustion process releases emissions and particles into the air (1).
When you melt a candle, you are simply liquefying the solid wax so it transforms into a liquid state. This can be done by placing the candle in a microwave, slow cooker, or double boiler. The wax will become a liquid as it is heated, but no flame or combustion will occur (2).
So melting a candle does not create any soot, smoke, or combustion byproducts. The wax just transitions from solid to liquid without any chemical reaction or burning taking place.
Melting Produces No Soot
Unlike burning, melting a candle does not involve any combustion. Without combustion, soot is unable to form. According to aluminatelife.com, soot is a byproduct of incomplete combustion, when candle wax does not burn fully. Soot contains black carbon particles that are released into the air. Since melting a candle involves simply liquefying the wax without lighting a flame, no combustion or burning takes place. Therefore, melting a candle does not result in any soot production.
This is advantageous because soot from burning candles contains lung irritants. According to everythingdawn.com, the black carbon present in soot can cause respiratory issues when inhaled. By avoiding combustion and soot production through melting, lung irritants are not introduced into the air.
Burning Releases VOCs
When a candle burns, it releases volatile organic compounds (VOCs) into the air. According to a study presented at the 2017 Pittcon Conference, burning candles emit VOCs like benzene and toluene [1]. Benzene is classified as a known human carcinogen by the EPA and WHO. Toluene is also hazardous and can cause irritation to the eyes, nose and throat. The type and amount of VOCs released depends on the candle wax composition. In general, paraffin wax candles produce more VOCs because paraffin is a petroleum byproduct. Beeswax and soy wax candles release fewer VOCs in comparison.
Melting Has No VOCs
Unlike burning, melting a candle does not release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) into the air. As explained on Healthline, “Burning candles releases volatile organic compounds and particulate matter into the air.” However, the process of melting by heating a candle does not combust the wax and therefore generates no VOCs (Healthline).
VOCs are carbon-based chemicals that can evaporate into the air we breathe. Studies have shown scented candles release various VOCs when burned, including potentially hazardous components (Ahn 2015). Thankfully, melting candles avoids this VOC production entirely. The melted wax simply transitions from solid to liquid form without any chemical breakdown or release of compounds. So melting a candle, rather than burning it, prevents VOC exposure and creates cleaner indoor air.
Burning Creates Indoor Pollution
Burning candles can significantly reduce indoor air quality by releasing pollutants like soot, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and lead into the air. A 2022 study published in Environmental Science and Pollution Research found that burning candles emitted concerning levels of fine particulate matter, formaldehyde, and other VOCs that exceeded safe limits [1]. The Environmental Protection Agency has also warned that lead-core wicks can cause dangerous lead contamination when burned [2]. These pollutants can irritate lungs, worsen asthma and allergies, and even increase cancer risk with long-term exposure.
Unlike burning, melting a candle avoids combusting the wax and wick which creates soot, VOCs, and other irritants. Melting also eliminates the fire hazard associated with open flames. For the cleanest and healthiest candle experience, melting is far superior to burning.
Melting Keeps Air Clean
Unlike burning, simply melting a candle does not release any soot or VOCs into the air. Melting a candle involves heating the wax just enough that it liquefies and pools around the wick, without actually igniting and combusting the wick itself. Therefore, no soot particles are generated from incomplete combustion when the wick is not lit.
According to research from the EPA, melting candles does not seem to have any negative effects on indoor air quality the way burning candles can (Source). Since no combustion occurs, melting candles does not produce any of the soot or VOCs that get emitted into the air when burning a candle. The melted wax stays contained in the candle holder and does not pollute the surrounding air.
Overall, melting a candle is very unlikely to worsen indoor air quality or have any harmful effects on one’s lungs and health. Simply warming the candle to liquefy the wax does not generate any soot, smoke or VOC emissions like burning the wick does. Therefore, melting candles provides the fragrance without negative impacts on indoor air.
Conclusion
After reviewing the evidence, it is clear that melting candles is healthier than burning them. When candles are burned, the flame produces soot, releases volatile organic compounds (VOCs) into the air, and creates indoor air pollution. However, melting candles avoids combustion and the byproducts associated with burning. Melted candles do not generate any soot or VOCs, keeping indoor air clean. The choice seems obvious – if you want to enjoy candles without the harmful effects of burning them, melting is the way to go. The experts agree that occasional candle burning does not pose a serious health risk, but melting candles eliminates any concerns entirely. For the healthiest home environment, opt to melt your candles instead of burning them.