Is Candle Wax Bad For The Environment?
Candles are used in many households for lighting, aromatherapy, and decorative purposes. While they can create a cozy ambiance, there are some environmental concerns related to candle production and use. The main component of most candles is wax, which is derived from petroleum, soybeans, beeswax, or palm oil. Certain types of wax, dyes, and wicks may release toxins when burned, contributing to indoor air pollution. There are also disposal issues if candle wax is not properly recycled. However, candles made from natural waxes like soy, beeswax, and vegetable-based waxes have less of an environmental impact. With mindful purchasing and careful use, candles can be an eco-friendly addition to the home.
Candle Wax Materials
Candles are made from various types of wax, each with their own properties and environmental impacts. The most common candle waxes are paraffin, soy, beeswax, and palm wax (Martha Stewart).

Paraffin wax is a petroleum byproduct made from crude oil refining. It is inexpensive and makes candles that burn cleanly, but there are concerns over its environmental impact since it is not biodegradable or renewable (The Spruce).
Soy wax is made from hydrogenated soybean oil. It is renewable and biodegradable. Soy candles burn slower and cooler than paraffin, but some find the natural scent unpleasant. Blending soy wax with other waxes can optimize its burn properties (Martha Stewart).
Beeswax is all-natural wax made by honey bees. It has a lovely honey aroma when burned. However, beeswax is expensive and can be challenging to work with due to its high melting point (The Spruce).
Palm wax comes from the fruit of palm trees. It is natural, renewable, and biodegradable. Palm wax makes high quality candles, but there are sustainability concerns around palm oil production (Martha Stewart).
Paraffin Wax Concerns
Paraffin wax is derived from petroleum and is considered a nonrenewable resource. The extraction, refining, and transportation of paraffin wax contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and environmental pollution [1]. When burned, paraffin candles release emissions like soot and toxins into the air, which can be hazardous to human health [2]. According to some estimates, burning a paraffin candle that weighs 140g can release up to 60mg of soot into the air.
Soy Wax Benefits
Soy wax provides some environmental benefits compared to other candle wax options. Soy wax is made from soybeans, which are a renewable crop. Soybeans can be replanted after harvest, making soy a sustainable raw material for candle production (Source). Soy wax is also biodegradable, meaning it will break down and decompose back into the environment when disposed of properly. The biodegradability of soy wax reduces waste and avoids some of the persistence issues caused by petroleum-based waxes (Source). Overall, the renewable and biodegradable nature of soy wax makes it one of the more eco-friendly candle wax choices currently available.
Beeswax and Palm Wax
Beeswax is considered one of the most sustainable waxes, as it is made by honey bees rather than heavily processed from petroleum. Beeswax is a renewable resource, though the supply is limited by the number of bee hives. Bee populations can be threatened by pesticides, diseases, and habitat loss, placing constraints on beeswax production. When sustainably sourced, beeswax provides a biodegradable, non-toxic option. However, pure beeswax candles can be costly compared to other waxes.
Palm wax, derived from the fruit of palm trees, emerged as an eco-friendly alternative to paraffin wax. But its production was linked to deforestation from palm oil farming. Sourcing palm wax sustainably requires adherence to certifications like the Roundtable on Sustainable Palm Oil (RSPO). As noted by CandleScience, sustainable palm wax offers a renewable, biodegradable material when responsibly farmed.
Wick Materials
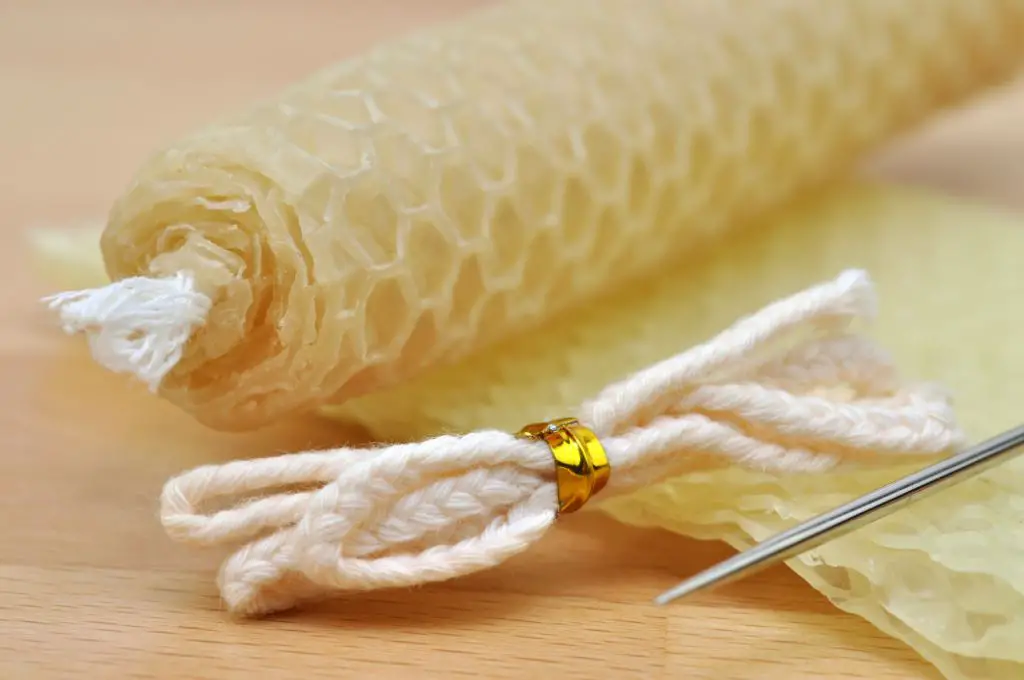

Wicks draw fuel up into the flame to keep the candle burning. Traditionally, wicks were made of cotton or paper fibers. However, cotton wicks can produce more soot so some candle makers now use wood or paper fiber alternatives. Zinc core wicks are also popular as the zinc helps keep the wick upright and rigid for an even burn.
Wood and paper fiber wicks tend to burn cleaner and produce less soot than traditional cotton wicks, so they have less impact on indoor air quality (La Lueur Candles). However, some versions still have a cotton core for stability. While zinc core wicks help prevent issues like tunneling, the zinc remains after burning and can end up in landfills. Therefore, more sustainable options are wood and paper fiber wicks, though unbleached cotton may be acceptable as well.
Candle Dyes and Scents
Many candles contain artificial dyes and synthetic fragrances which can release potentially harmful volatile organic compounds (VOCs) into the air when burned. The chemical compounds in these candle additives can irritate the eyes, nose and throat. Exposure to high concentrations of VOCs may also cause headaches, nausea or dizziness.
Certain artificial dyes and synthetic fragrances have been linked to more severe health effects like respiratory problems, organ damage or cancer. However, research on candle emissions is limited. The levels of chemical exposure from occasional candle burning may not be significant enough to cause major health issues for most people.
Those concerned about potential toxicity from candle dyes and scents may want to opt for candles made with natural plant-based dyes and essential oils instead of artificial ingredients. As with anything, moderation is key – burning too many candles too often in an unventilated space can lead to unhealthy buildup of particulates and VOCs.
Proper Candle Disposal
When disposing of candles, it’s important to do so in an environmentally friendly way. Here are some tips for proper candle disposal:
Let the candle wax fully cool before attempting to dispose of it. Pouring hot wax down drains or into trash cans can lead to clogs and other issues. Allow at least 24 hours for the wax to fully harden after blowing out the candle.
Reuse candle jars, tins, and other containers. Glass jars can be repurposed for food storage or as drinking glasses. Metal tins make great organizers. Get creative and find ways to reuse candle vessels. Some candle companies even offer recycling programs for their containers. Just be sure to fully remove all wax first.

Avoid putting wax down drains or in regular trash cans. As mentioned, hot wax can clog pipes. Candle wax wrapped in trash bags can also melt and leak in landfills. Instead, let hard wax go in the trash or find specialty recycling for wax.
Check for candle recycling programs in your community. Some municipal recycling centers and waste management companies accept old candle wax and jars. Call ahead to see if such options exist locally. This way materials get properly handled.
Upcycle old wax into new candles. Collect wax drippings and meltdown used candles to create handmade recycled candles. This repurposes the wax into something useful.
Ultimately, being mindful when disposing of candle materials makes a difference. Follow these tips to reduce waste and reuse what you can.
Reducing Candle Waste
There are a few practical ways you can reduce candle waste in your home. Here are some top tips:
Use natural, reusable materials. Look for candles made from soy, beeswax or other natural waxes, and ensure the jar or container is glass, ceramic, tin or other recyclable material. Reuse the jar when finished by cleaning thoroughly and filling with dried flowers, spices, or other household items (Social Innovation Seed Fund recipients launch their venture, 2022).
Buy candles with cotton or wood wicks instead of metal wicks which cannot be composted. Opt for candles with reusable metal tins or look for brands that will take back the glass jar for recycling when finished.
Consider making your own candles at home using old jars and natural wax. There are many DIY tutorials online for rolling beeswax sheets or melting soy wax flakes to create homemade candles.

When lighting candles, trim wicks to 1⁄4 inch before burning to avoid excessive smoking and burning. Extinguish candles when 1⁄2 inch of wax remains to reduce wasted wax. Never burn a candle all the way down as this can damage the container.
Conclusion
In summary, traditional paraffin wax candles do raise some environmental concerns due to their petroleum-based ingredients and potential to emit toxins when burned. However, there are more eco-friendly candle options available, including soy, beeswax, and palm wax candles. Consider buying candles made from natural waxes and wicks to reduce your environmental impact.
When buying candles, check labels for ingredients. Look for candles made from soy, beeswax, or sustainably-sourced palm oil. Avoid paraffin candles when possible or ensure proper ventilation when burning them. Dispose of used candles responsibly by extinguishing wicks, allowing wax to fully harden, and placing in the trash – never pour hot wax down drains. Making your own candles from eco-friendly ingredients is another great option for minimizing waste.
While no candle is 100% environmentally inert, we can reduce their impact through mindful purchasing and burning habits. Seek out natural, non-toxic candles and use them moderately, with proper ventilation. Dispose of them properly when finished to keep our homes and planet healthy and sustainable.