How Do You Melt Candles Properly?
Melting candles allows you to customize candle colors, scents, and shapes. It also enables repurposing candle wax from finished candles into new candles or other items. Melting and combining different candle waxes and fragrances lets you create your own signature scents and colors. There are many benefits to melting and making your own candles:
Burning candles can provide relaxation, self-care, and numerous health benefits. The Mayo Clinic notes that exposure to a candle’s flame “may induce relaxation and help decrease anxiety and emotional volatility.” The soft glow of a candle creates a peaceful ambiance that can lower stress levels and promote mindfulness. Inhaling the aromatic compounds in scented candles can also positively affect mood and cognition. Studies have found lavender and chamomile aromas can enhance calmness and improve sleep quality. Overall, burning candles can be part of a holistic self-care routine that encourages relaxation, presence, and peace of mind (https://www.purcellandwoodcock.com/blog/benefits-of-burning-candles.html).
Safety Precautions
Melting candles requires some safety precautions to avoid fire hazards and injuries from hot wax. According to the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), candles are responsible for an estimated average of 9,300 home fires each year, so proper handling is important (https://www.nfpa.org/News-and-Research/Data-research-and-tools/US-Fire-Problem/Candle-fires-and-homes).
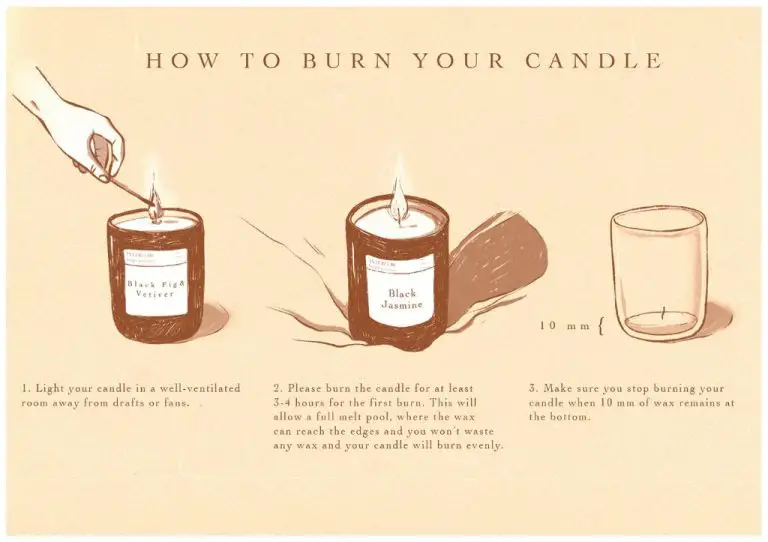
Always melt candles in a well-ventilated area and avoid drafts or air currents that can cause rapid or uneven burning (https://candles.org/fire-safety-candles/). Never leave burning candles unattended and keep them away from flammable materials like curtains or upholstery.
Melted wax can reach temperatures up to 185°F, so use caution to avoid burns (https://aromasparks.com/pages/candle-waxmelt-care-and-safety). Wear heat-resistant gloves when handling hot containers of melted wax. Keep children and pets away from melting and pouring processes.
Choosing a Melting Vessel

When melting candles, it’s important to choose the right melting vessel. The material of the vessel is especially important since different materials have different melting points and heat transfer properties. There are a few common materials used for candle melting pots:
Metal: Stainless steel and aluminum are popular metals for melting vessels. They conduct heat well for efficient melting. Stainless steel can withstand higher temperatures than aluminum. However, some metals can react with candle waxes. Make sure to use food-grade stainless steel.
Glass: Glass is commonly used for candle melting pots. It allows you to monitor the melting wax and is inert so won’t react with the wax. However, glass can crack if heated too quickly. Use tempered glass pots and slowly bring the wax to temperature.
Ceramic: Ceramic pots are also popular for candle making because they hold heat well. However, they don’t conduct heat as quickly as metal so melting may take longer. Make sure to get a glazed ceramic pot that won’t absorb oils from the wax.
The size, shape, and capacity of the melting vessel is also important. Choose a vessel large enough to hold the volume of wax you want to melt. Tall, narrow pots melt wax faster since more surface area is exposed to the heat. Wide, shallow pots may take longer but allow you to melt larger volumes.
For safety, opt for a pot with a pouring spout. Always place the pot on a silicone mat or baking sheet in case of spills. Choose a melting vessel appropriate for your heat source as well. You can find a variety of candle melting pots and wax melters made for stovetops or electric melters.
Some good options are stainless steel pots (https://www.amazon.com/Electric-Melter-Melting-Pouring-Quick-Pour/dp/B09NVMTKMV), ceramic melting pots, and pouring pots with spouts designed for candle making. Avoid non-food grade metals, thin glassware, or plastic containers.
Prepping the Vessel
Before melting wax in any container, it’s crucial to properly clean and prep the vessel. All traces of dust, dirt, soap residue, oils, etc. should be thoroughly washed away with hot water and dish soap. Allow the container to completely air dry.
For glass and metal containers, no further preparation is needed. However, for porous materials like terra cotta, concrete, or wood, the vessel should be coated with a thin layer of oil to prevent wax from penetrating the material. Choose a food-safe oil like coconut, olive, or vegetable oil. Using a paper towel or clean cloth, rub a small amount of oil over the entire interior surface of the container. Remove any excess oil by wiping again. Allow the oil to fully absorb before adding wax (Source).
Proper prep allows the melted wax to release cleanly from the container without sticking or residue. Always inspect vessels and address any cracks, damage, or oil spots prior to pouring in wax.
Choosing the Heat Source
There are several options for safely melting candle wax, each with their own pros and cons:
Stovetop
Using a stove burner is a common way to melt candle wax. Be sure to select a vessel that fits securely on the burner. Monitor the temperature closely so the wax doesn’t overheat. Stovetops provide consistent heat that can keep wax melted for extended periods (Source).
Microwave
A microwave can quickly melt candle wax but the heat can be uneven. Microwave in short intervals, stirring in between to prevent hot spots. Glass and ceramic vessels work best (Source).
Candle Warmer
Electric candle warmers apply gentle heat from underneath to melt wax without risk of scorching. Warmers allow melted wax to stay liquid for hours while working (Source).
Double Boiler
A double boiler uses steam from heated water to gently melt wax. This prevents wax from overheating. Double boilers provide even heat distribution (Source).
Preparing the Candles
Before melting candles, it’s important to prep them properly. First, trim the wicks to 1⁄4 inch length using scissors or clippers so they don’t catch fire while melting. Next, scrape any wax off the bottom of the candles. This helps get all the wax out when melting. Finally, chop large candles into smaller pieces, about 1-2 inches each. This allows the wax to melt faster and more evenly. According to an article on PopSci, chunking candles into bite-size pieces can help melt wax faster than keeping candles whole. Make sure to remove any candle holders or metal pieces embedded in the candles before melting them down. With wicks trimmed, wax scraped off, and candles chopped up, you’ll be ready for the melting process.
Melting the Candles
Melting candles properly is crucial for achieving an even burn and optimal scent throw. Follow these step-by-step instructions for melting candles successfully:
First, fill your melting vessel about halfway with water and place it over low heat. Glass and metal vessels work best as they evenly distribute heat. Avoid plastic which can melt and contaminate the wax (Source).
Next, place your wax in a separate smaller container and set it in the water bath. Never place wax directly in the water or over direct heat. This can scorch the wax. The water will gently heat the wax to a liquid state (Source).
Stir the wax occasionally with a spoon or chopstick. Once fully melted, remove the wax container from the water bath. Avoid overheating which can diminish scent and discolor wax.
Test the wax temperature with a thermometer, aiming for 185-200°F. This ensures proper pouring viscosity without being dangerously hot.
Now the wax is ready for combining, mixing, and pouring into candle vessels or molds. Work carefully to avoid spills and burns. Let candles fully cool and cure before lighting.
Combining and Mixing
Once all the candles are fully melted, you can combine them into one vessel for mixing. Use a clean silicone spatula or wooden spoon to stir the melted wax. Stir slowly and thoroughly to evenly distribute the wax colors and scents throughout the mixture. According to this Reddit thread, you can add a bit of beeswax to help harden the final product if desired.
Next, blend in any additional fragrance oils or candle colorants as needed. Add these slowly, a little at a time, stirring continuously. Adding too much fragrance at once can cause seizing. Let the wax fully incorporate each addition before moving on. Take care not to spill or splash the wax when mixing.
Mix until the melted wax is a homogeneous liquid with an even distribution of color and scent. At this point, it’s ready to be poured into containers or molds!
Pouring and Cooling
Once the wax is fully melted and mixed to the desired scent and color, it’s time to carefully pour it into candle containers or molds. When pouring, it’s important to maintain the proper pouring temperature for the wax you are using. Paraffin wax, for example, should be poured between 185-200°F (https://lonestarcandlesupply.com/prepare-wax-for-pouring/). Soy wax can be poured between 135-165°F.
Pour the wax slowly and steadily into each container, leaving about 1/4″ of headspace at the top. This allows room for the finished candle to form a smooth, even surface as it cools and shrinks slightly. Avoid splashing or agitating the wax too much as you pour.
Proper cooling is critical for achieving a smooth candle surface and clean burn. Allow the candles to cool undisturbed until a thin skin forms on top. At this point, you can gently smooth over any sharp edges or divots with a heat gun. But be careful not to overheat the surface. As the candle continues cooling, avoid drafts which could create divots or sink holes.
For best results, allow the candles to cool at room temperature for 12-24 hours before testing the burn. This allows the wax to fully set up and stabilize (https://coogarproducts.com/better-pouring-methods-for-better-soy-candles/). Proper pouring and cooling helps ensure your finished candles have an attractive surface and clean, even burn.
Storing and Using
After melting your candles, it’s important to properly store the leftover melted wax so it stays usable for future projects. According to this source, you should store melted wax in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and heat. An ideal storage spot is a cupboard or closet. You can pour the wax into a heatproof glass or metal container with a lid.
Don’t throw away leftover melted wax! There are many ways to reuse it for crafts and hobbies. Some ideas are to make new candles or wax melts, wax seal stamps, or candle holders. Melted wax can also be used to lubricate drawers and hinges. Be creative and find helpful uses for the wax rather than letting it go to waste.