Are Lighting Candles Good?
Candles have been used for thousands of years to provide light and create ambiance. Today, candles remain popular for their beauty and versatility – they can create a relaxing or romantic atmosphere, mask odors, repel insects, serve as part of religious rituals, or provide emergency lighting during power outages. Candles come in a variety of shapes, sizes, colors and scents to suit nearly any purpose. With proper care, candles can be an enjoyable part of daily life. This article explores the benefits and potential downsides of using candles.
History of Candle Use
The earliest known use of candles originated in Ancient Egypt around 3,000 BC, where they were made from beeswax (History, 2022). Ancient Egyptians used candles in their homes at night, and also for spiritual or ceremonial purposes. Candles were placed in tombs of pharaohs and depicted in hieroglyphics on tomb walls.
In Ancient Rome around 1 AD, candles were made from tallow, which is rendered fat from cows or sheep (Wikipedia contributors, 2023). The Romans developed candle wicking methods using papyrus and put candles on birthday cakes. Candles continued to hold cultural significance and were used in early Christian ceremonies in Rome.
In Medieval times from 476 AD – 1492 AD, candlemaking became an established trade with professional chandlers (History, 2022). Candles transitioned from being made by hand to production via casting or dipping molds. Beeswax remained the preferred material, while tallow candles were more commonly used by the poor.
The early Colonial American period from 1492 – 1776 saw a shift back to homemade candlemaking, as well as early experimentation by colonists with new materials like bayberry and spermaceti wax (Creative Candles, 2022). The Industrial Revolution from the late 18th century brought about mechanized production and paraffin wax.
References:
– History. (2022). https://candles.org/history/
– Wikipedia contributors. (2023). https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/History_of_candle_making
– Creative Candles. (2022). https://creativecandles.com/blogs/blog/a-history-of-candle-use
Benefits of Candles
Burning candles can provide many benefits through enhancing ambiance, utilizing aromatherapy, creating mood lighting, and promoting relaxation.
Candles can greatly improve the aesthetics and ambiance of a space. Their warm, flickering glow creates a cozy atmosphere and pleasant scent. The soft lighting candles provide allows people to unwind and feel comfortable [1]. Candles also add style and decoration to living spaces.
Scented candles provide aromatherapy benefits as the fragrance fills the air. Studies show aromatherapy with candles can reduce stress, anxiety, and depression while improving mood and relaxation [2]. The scents can stimulate the brain in positive ways.
Candles are an easy way to create mood lighting. The ambient glow provides a romantic or relaxing vibe depending on the scent and setting. Candlelight fosters intimacy and feelings of calm.
Burning candles helps many people feel at ease. The low lighting and aromatherapy promote a relaxed state for activities like meditation, yoga, reading or conversation. The simple act of lighting a candle can mark the transition to unwinding after a stressful day [3].
Potential Downsides of Candles
While candles can provide benefits, they also come with some potential downsides to be aware of. The main concerns with candles involve fire hazards, air pollution, soot, and allergies.
One of the biggest risks with candles is potential fire hazards, as having an open flame indoors always presents some risk. According to WebMD, around 11,000 fires per year in the U.S. are started by candles. It’s important to take precautions like keeping candles away from flammable materials, not leaving them unattended, and properly extinguishing them.
Burning candles, especially scented ones, can also contribute to indoor air pollution and release compounds like soot and volatile organic compounds into the air. Long term exposure to these pollutants may irritate the airways or worsen respiratory conditions like asthma according to Healthline. Soot buildup can also dirty walls and surfaces.
The scents and chemicals released from candles may also trigger allergic reactions or headaches in some individuals who are sensitive. It’s best to choose unscented, natural, or soy-based candles if you experience reactions.
Safety Tips
When using candles, it’s important to follow key safety tips to prevent fires, injuries, and other accidents (National Fire Protection Association). Here are some best practices:
Proper placement is crucial. Keep candles at least 12 inches away from anything flammable like curtains, furniture, bedding, papers, books, and decorations (FM Global). Avoid placing candles near drafts which can cause rapid, uneven burning. Position candles on a sturdy, nonflammable holder. Never put candles on a shelf above eye level.
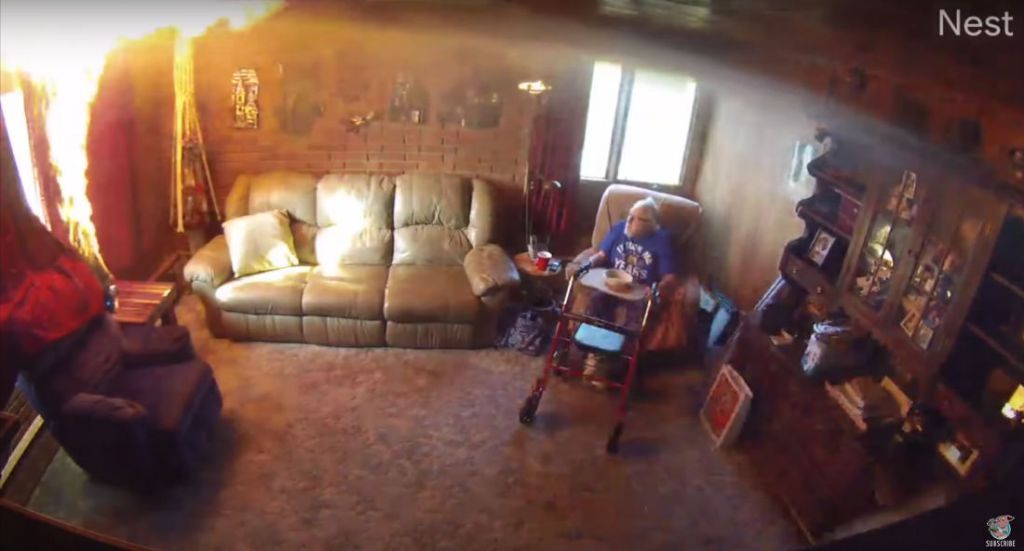

Always supervise candles when lit. Never leave a burning candle unattended or sleep in a room with candlelight (National Candle Association). Extinguish candles before leaving a room or going to sleep.
Use nonflammable holders that are heat resistant. Glass, metal or ceramic holders work best. Make sure the candle fits well inside the holder and the holder is placed on a stable, level surface.
Allow candles to cool completely before moving or extinguishing. Wet your fingers and gently pinch the wick if you need to put out the flame. Never blow out candles which can cause wax droplets to scatter.
Different Types of Candles
There are many different types of candles available in a range of wax varieties, shapes, sizes, and scents. Some of the most popular candle types include:
Wax Varieties:
- Paraffin – Most common candle wax made from petroleum. Inexpensive and readily available.
- Soy – Made from soybeans. Clean burning and biodegradable.
- Beeswax – Made from beeswax. Natural, non-toxic, and aromatic.
- Palm – Made from palm oil. Hard wax with high melting point.
- Gel – Translucent, flexible wax. Used for container candles.
Shapes/Sizes:
- Pillar – Tall cylindrical candles. Range from small votives to large pillars.
- Taper – Skinny, cylindrical candles. Used in candelabras.
- Tealight – Small, round candles in metal cups with short wicks.
- Container – Wax poured into glass or metal containers.
- Floating – Candles designed to float on water.
Scented vs. Unscented:
- Scented – Infused with essential oils. Provide aroma when burned.
- Unscented – No added fragrance. Allow natural scent of wax.
There are many specialty candle varieties available like gel candles, carved candles, and more. The options are nearly endless for designing candles to suit your needs and preferences.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of candles depends greatly on the materials used to make them. Conventional paraffin wax candles are made from petroleum, a non-renewable fossil fuel. Extracting and refining petroleum to make paraffin wax generates greenhouse gas emissions that contribute to climate change [1]. Beeswax and soy wax, on the other hand, come from renewable sources like bees and soybean plants.
In terms of carbon footprint, beeswax candles have the lowest impact since they can be produced locally using sustainable beekeeping practices. Soy wax also has a smaller carbon footprint than paraffin [2]. Transporting and refining petroleum into paraffin wax is very energy-intensive.
When it comes to recycling, all candle wax can technically be reprocessed and reused to make new candles. However, paraffin is much more commonly recycled than natural waxes. Paraffin can be separated from candle containers and recycled back into new candles, while beeswax and soy wax are rarely collected for reuse [3]. Opting for renewable and recyclable candle materials can help reduce environmental impact.
Cost Considerations
The price range for candles can vary greatly depending on factors like the type, size, ingredients, and where it’s sold. Here’s an overview of typical price ranges:
Smaller candles like votives or tealights often range from $1-$5. Pillar candles are usually $5-$15 depending on the height and diameter. Standard 8-12oz jar or tumbler candles tend to range from $10-$25 in most retail stores. For artisan and boutique candles made with premium ingredients, prices typically start at $15 and can go up to $50 or more.
In terms of cost per hour of use, this also varies a lot. Tealights may only burn for 4-6 hours and cost around $0.25-$0.50 per hour. A long burning 12oz or 16oz jar candle may burn for 60-80 hours and cost $0.15-$0.25 per hour. Luxury candles with high-quality oils often have excellent scent throw even when not lit, providing aroma benefits for days. Factors like container style and wax quality greatly affect burn times.
When evaluating candle costs, consider not just the price but also the quality, burn duration, and overall experience. Well-made candles provide delightful ambiance and home fragrance. Focusing too much on price per hour can miss the experiential benefits.
Sources:
https://www.candlescience.com/how-to-price-your-candles/
https://villagecraftandcandle.com/blogs/news/how-to-price-your-candles
Alternatives to Candles
For those looking to avoid the potential risks of burning candles, there are several effective alternatives that can create a similar ambiance without an open flame.
LED Lights
LED string lights and lamps provide a soft glow without the need for a wick or wax. They come in a variety of shapes, sizes and colors to suit any décor. LEDs consume very little energy and don’t emit smoke or scent like traditional candles (source).
Essential Oil Diffusers
Essential oil diffusers disperse your choice of scented oil into the air to fill a room with fragrance. They are flameless, safer for pets and children, and the oils can provide aromatherapeutic benefits. Diffusers allow you to switch between scents and avoid smoky residue from burnt candles (source).
Natural Light
Opening blinds, curtains or shades to allow natural sunlight in creates a bright and uplifting environment. Sunlight boosts vitamin D and regulates circadian rhythms. For nighttime, keeping blinds open can let in moonlight. Natural light provides a mood boost without any of the drawbacks of candles (source).
Conclusion
Overall, there are several potential benefits as well as some drawbacks to using candles. Candles can provide soothing ambiance, pleasant natural scents, and create a relaxing environment. However, they can also pose fire hazards if left unattended or placed near flammable materials. There are also environmental impacts from paraffin wax and concerns around air quality with excessive soot.
To enjoy candles responsibly, it’s best to use high quality, clean burning beeswax or soy candles rather than paraffin. Place candles in sturdy holders on uncluttered surfaces, away from drapes or furniture. Never leave burning candles unattended and keep wicks trimmed to 1⁄4 inch to prevent excess smoke. Consider battery operated flameless candles for unattended or longer duration use. Use candles in moderation, ventilate the room well, and carefully extinguish when finished. With mindful use, candles can be an enjoyable way to set ambiance while minimizing risks.